Upper Tail Probability Table
The graph of the normal probability distribution is a bell-shaped curve as shown in Figure 73The constants μ and σ 2 are the parameters. How to Draw a Normal Probability Plot By Hand.
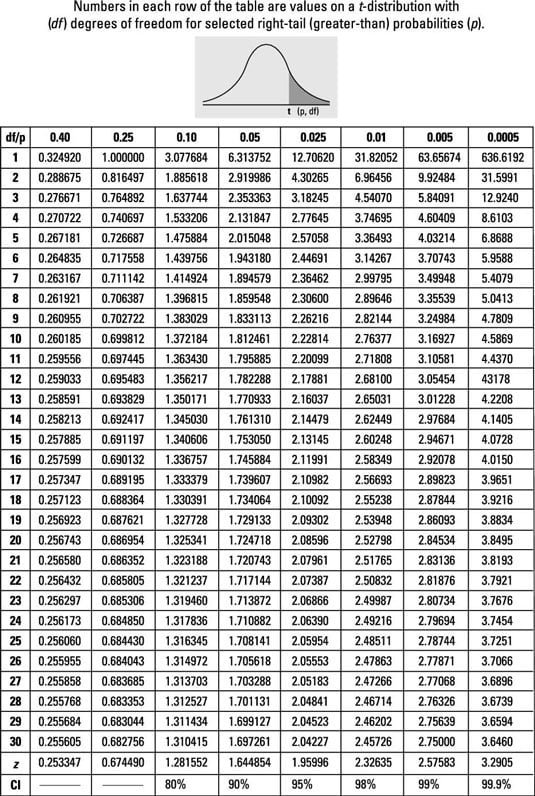
How To Use The T Table To Solve Statistics Problems Dummies
Look up the z-value in a z-table and the value you find in the body of the table represents the area under the probability distribution curve to the left of your positive z.
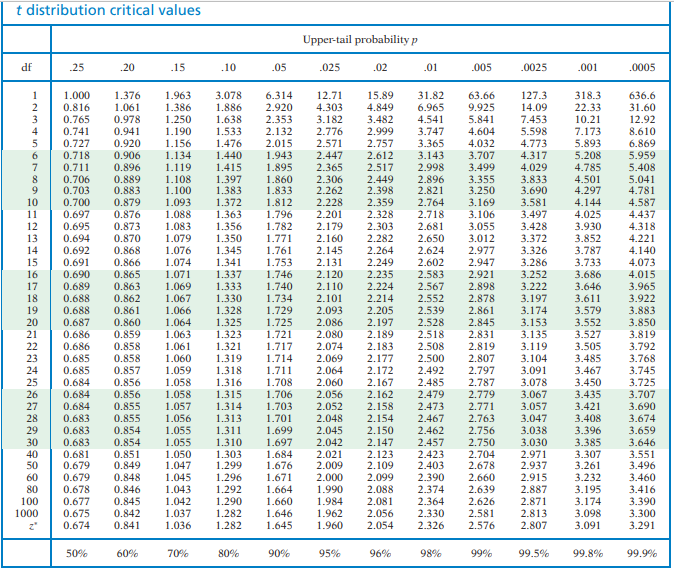
. The p-value is the probability that the data could deviate from the null hypothesis as much as they did or more. In terms of a random experiment this is nothing but randomly selecting a sample of size 1 from a set of numbers which are mutually exclusive outcomes. 2 The commuter trains on the Red Line for the Regional Transit Authority RTA in Cleveland OH have a waiting time during peak rush hour periods of eight.
The critical zvalue for a probability of 005 in the upper tail is 165. Their name introduced by applied mathematician Abe Sklar in 1959 comes from the. For two-sided tests the test statistic is compared with values from both the table for the upper-tail critical values and the table for the lower-tail critical values.
Consequently the p-value measures the compatibility of the data with the. D Find the probability of waiting eight minutes exactly. The significance level α is demonstrated with the graph below which shows a chi-square distribution with 3 degrees of freedom for a two-sided test at significance level α 005.
For a one-tailed test first calculate your z-test statistic. So you look up the zvalue for a probability of 095. Remember that Table 2 in Statistics Tables gives areas of the curve below z.
Six-line figures of yin broken or yang solid lines and commentaries on them. For a 95 confidence interval the area in each tail is equal to 0052 0025. Which numerical summary would you like to calculate for each group.
Take your significance level and subtract it from 1. All members of a class are represented by their class marks when calculating most statistics for a frequency distribution table. Use the formula TINVprobability degrees of freedom.
Copulas are used to describemodel the dependence inter-correlation between random variables. Enter the given contingency table of observed values in cells A1 through F4. Press Enter to.
The binomial coefficient multiplies the probability of one of these possibilities which is 12²12² 116 for a fair coin by the number of ways the outcome may be achieved for a total probability of 616. Use that column in the chi-square table to find the left-tail critical value. Here the sample space is 123456 and we can think of many different.
The Lower 950 and the Upper 950 columns give the lower and upper endpoints of the 95 confidence intervals for the y-intercept and slope for the independent variable. The value z representing the point on the standard normal density curve such that the probability of observing a value greater than z is equal to p is known as the upper p critical value of the standard normal. The upper class limits are the highest values that can be in the bin.
Calculate f i i-0375n025 where i is the position of the data value in the ordered list and n is the number of observations. For this test the rejection region of 005 would be entirely within the upper tail. If there is a.
Time Distances and dimensions Obligation need possibility and probability Possession and giving Movement and speed Texture brightness weight and density English Vocabulary in Use Upper-intermediate 3 Connecting and linking words 61 Time. For a one-tailed upper-tail test. B Find the probability of waiting between two and five minutes.
Connecting words and expressions 62 63 Condition Cause reason purpose and result 64 65 66 67. The lower class limit is the lowest value in a bin a particular category. For example if your significance level is 005 then use 1 005 095.
In probability theory and statistics a copula is a multivariate cumulative distribution function for which the marginal probability distribution of each variable is uniform on the interval 0 1. A typical example for a discrete random variable D is the result of a dice roll. The complete table of critical values of Z for upper lower and two-tailed tests can be found in the table of Z values to the right in Other Resources.
Next the test statistic is used to conduct the test using either the p-value approach or critical value approach. Arrange your x-values in ascending order. I Ching divination is a form of cleromancy applied to the I ChingThe text of the I Ching consists of sixty-four hexagrams.
Namely μ is the population true mean or expected value of the subject phenomenon characterized by the continuous random variable X and σ 2 is the population true variance characterized by the continuous random variable X. You may want to watch the Excel video below as it explains many of these steps in more detail. For an upper-tail test z.
The possibilities are HHTT HTHT HTTH TTHH THHT THTH where H represents a head and T represents a tail. Area in one tail. The form can easily be identified by looking at the alternative hypothesis H a.
There are two main methods of building up the lines of the hexagram using either 50 yarrow sticks or three coins. A midpoint is defined as the average of the upper and lower class limits. Lower tail upper tail or two-tailed.
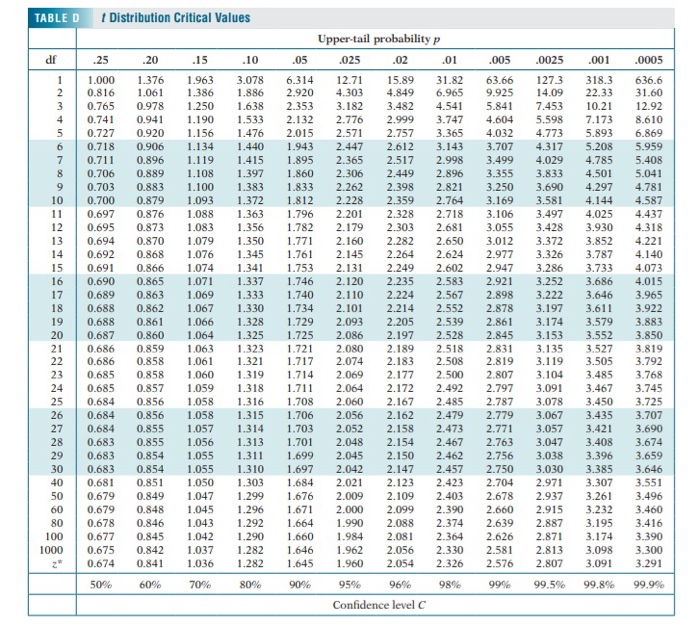
The column and row intersections are the right-tail critical values for a given probability and degrees of freedom. Probability Distributions of Discrete Random Variables. C Find the probability of waiting between seven and ten minutes.
The particular steps taken in each approach largely depend on the form of the hypothesis test.
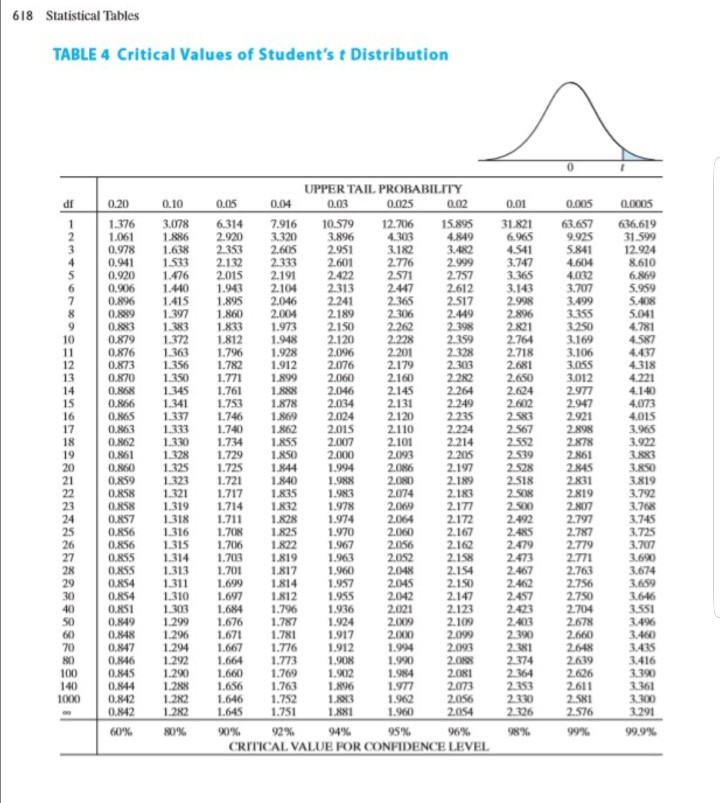
Degrees Of Freedom Awnnnnnnnnnn Upper Tail Chegg Com
Solved The Skull Width Of A Population Of Rodents Follows A Chegg Com
Solved My Notes Ask Your Teacher 06 Points Mintrosat97 Chegg Com

T Distribution Critical Values Upper Tail Probability Chegg Com


Comments
Post a Comment